If you’re an avid home cook or baker, you may have wondered: can ceramic bowls go in the oven? This common question arises as we seek to simplify our kitchen routines and make the most of our cookware. In this article, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of using ceramic bowls in the oven, exploring the types of ceramic that are oven-safe and the factors to consider when baking or cooking with them.

We’ll also discuss tips for safely using ceramic bowls in the oven, including how to avoid thermal shock and ensure even heat distribution. So, whether you’re preparing a cozy casserole or whipping up a batch of homemade bread, let’s uncover the truth about ceramic bowls and their role in your oven adventures!
Table of Contents
Common Use of Ceramic Bowls for Food
Ceramic bowls are incredibly versatile, serving as a canvas for both chefs and home cooks to present their culinary creations. They are commonly used for a variety of food applications, from mixing ingredients to serving hot and cold dishes. The aesthetic appeal of ceramic bowls adds a touch of elegance to everyday dining, making them popular for serving soups, salads, pasta, and desserts.
Their ability to retain heat also makes them ideal for keeping foods warm at the table. Furthermore, their resistance to absorbing odors and flavors ensures that each dish maintains its true taste and aroma, enhancing the overall dining experience. Whether it’s a hearty stew that’s been gently simmered or a vibrant salad freshly tossed, ceramic bowls play a crucial role in food preparation and presentation.
Can Ceramic Bowls Go in The Oven?
The short answer is, yes, some ceramic bowls can go in the oven, but not all are created equal. The key to safely using ceramic bowls in the oven lies in understanding the type of ceramic they are made from. Most high-quality ceramics labeled as oven-safe can withstand high temperatures without cracking or shattering. However, the risk comes with ceramics that are not explicitly marked as suitable for oven use. These may have been crafted with different clays or glazed with materials not designed to endure the thermal stress of oven heat.
Temperature changes, particularly rapid heating or cooling, can cause a process known as thermal shock, leading to cracks or even complete breakage. Therefore, it’s crucial to check the manufacturer’s instructions or look for an “oven-safe” label before placing ceramic bowls in the oven. Oven-safe ceramics are specifically designed to handle a wide range of temperatures, making them a safe choice for baking, roasting, or serving hot food directly from the oven to your table.
Differences Between Different Types of Ceramics
When discussing ceramics that can be safely used in an oven, it’s essential to understand the distinctions between the various types of ceramics available. These differences can significantly influence a ceramic bowl’s ability to withstand oven temperatures without sustaining damage.
Earthenware:

Earthenware is one of the oldest materials used in pottery, characterized by its porous nature and relatively low firing temperature. While earthenware can be glazed to make it more durable, it’s less suited for oven use compared to other ceramics because of its susceptibility to thermal shock.
Stoneware:
Stoneware is a denser, more durable type of ceramic that is fired at higher temperatures than earthenware. This results in a sturdier material that is less porous and more resistant to thermal shock, making stoneware pieces generally safer for oven use.
Porcelain:
Porcelain is made from a refined clay and fired at even higher temperatures than stoneware, creating a non-porous, translucent, and very durable material. Porcelain has a high resistance to thermal shock and is often safe for oven use, although it’s always best to check for an oven-safe label due to variations in manufacturing.

Terracotta:
Terracotta, often associated with plant pots, is another type of earthenware. It is usually not glazed and has a rustic appearance. While it can be used for cooking in specific contexts (like baking bread), it’s generally not recommended for regular oven use unless explicitly labeled as oven-safe.
Understanding these differences is crucial for home cooks and bakers to select the right ceramic bowls for their cooking needs, ensuring safety and longevity of the cookware.
Characteristics of Oven-Safe Ceramic Bowls
Thick Walls:
Oven-safe ceramic bowls typically feature thicker walls than those not meant for oven use. This added thickness helps in evenly distributing heat and reduces the risk of thermal shock.
Even Glaze:
A smooth, even glaze not only contributes to the aesthetic appeal of the bowl but also plays a crucial role in its heat resistance. An uneven glaze can cause uneven heating, which increases the risk of cracking.
Oven-Safe Label:
Perhaps the most straightforward way to identify if a ceramic bowl is oven-safe is to look for a label or marker indicating as such. Manufacturers usually specify if the ceramic can withstand oven temperatures.
No Metallic Paint:
Ceramics decorated with metallic paint or finishes are not suitable for oven use, as these materials can spark or deteriorate under high heat. Oven-safe bowls generally avoid these decorative elements.
Sturdy Base:
A stable and sturdy base is critical for oven-safe ceramics. This ensures that the bowl sits securely in the oven without rocking or tilting, which could lead to uneven cooking or spillage.
Safety Precautions for Using Ceramic Bowls in the Oven
Always Preheat the Oven:
To prevent thermal shock, always preheat your oven before placing your ceramic dish inside. This helps to gradually acclimate the ceramic to the increased temperature.
Avoid Sudden Temperature Changes:
Do not transfer a ceramic bowl directly from the refrigerator to the oven or vice versa. Allow the dish to come to room temperature first to minimize the risk of thermal shock.
Use Oven Mitts or Potholders:

Ceramic retains heat well, which means bowls can remain hot long after being removed from the oven. Always use oven mitts or potholders when handling to protect your hands from burns.
Place on a Baking Sheet:
For added stability and to catch any potential spills, consider placing your ceramic bowl on a baking sheet before putting it in the oven. This also makes it easier to remove the dish once cooking is complete.
Check for Damage Before Use:
Inspect your ceramic bowls for any cracks, chips, or damage before each use. Even minor damage can lead to breakage when subjected to the high temperatures of an oven.
Avoid High Broiler Settings:
Unless specifically stated by the manufacturer, avoid using ceramic bowls under high broiler settings. The intense heat from a broiler can cause damage to some ceramics.
Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions:
Always adhere to the guidelines provided by the manufacturer regarding oven use. These instructions can vary between different types and brands of ceramics.
How to Avoid Thermal Shock
Gradual Temperature Changes:
Always aim for gradual temperature changes. When using an oven, avoid placing a cold ceramic directly into a hot oven. Instead, allow the ceramic to come to room temperature, or place it in the oven before it’s turned on, and then gradually increase the heat.
Avoid Direct Heat Sources:
Never place ceramics directly on a stovetop burner or under a broiler unless the manufacturer explicitly states that it’s safe to do so. Direct, intense heat sources increase the risk of thermal shock.
Room Temperature Storage:
Store your ceramics in a location that maintains a relatively constant, room temperature. Sudden changes in the storage environment can predispose the material to thermal shock when later heated.
Use a Water Bath for Drastic Changes:
If a recipe requires a sudden change in temperature, consider using a water bath to buffer the direct heat. This technique is particularly useful for delicate baking processes that involve ceramics.
Warm Liquids:
If you need to introduce a liquid into a ceramic bowl that’s already hot, ensure the liquid is warm rather than cold. The drastic temperature difference between hot ceramics and cold liquids can trigger thermal shock.
Even Heating:
When possible, heat your ceramics in a manner that ensures even temperature distribution. Uneven heating can create stress points in the material, leading to cracks or breaks.
Why Some Bowls Shatter
At the heart of understanding why some bowls shatter under heat lies the concept of thermal expansion. Different materials expand at different rates when subjected to heat. Ceramics, by their nature, are made from clay that is molded and then fired at high temperatures to achieve their final form. However, not all ceramics are created equal, and their composition, along with the way they were fired, can greatly affect their ability to withstand thermal stress.
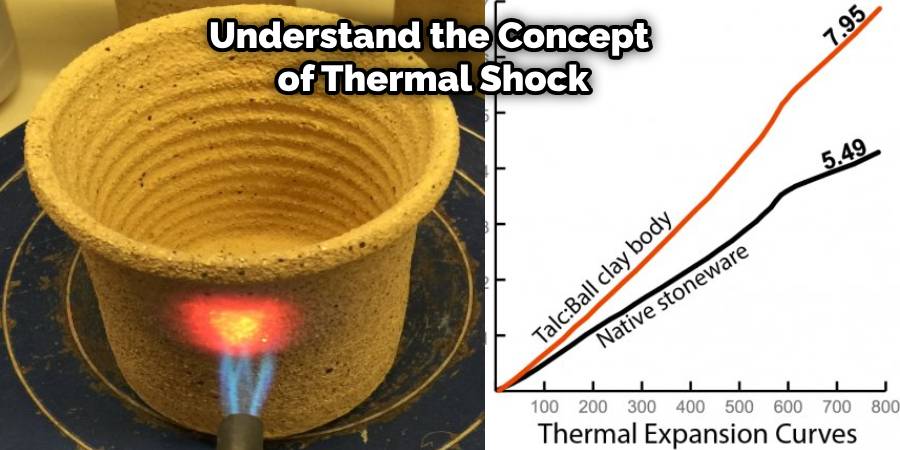
When a bowl is exposed to rapid temperature changes or uneven heating, the stress caused by expansion cannot be evenly distributed throughout the item. This results in what is known as “thermal shock,” which can cause the material to crack or even shatter. Bowls that are thinner, have irregular shapes, or contain flaws such as air bubbles or uneven thickness are particularly susceptible to shattering due to thermal shock.
In addition, bowls that are not specifically designed to be oven-safe may have been treated with glazes or contain materials that expand at different rates than the ceramic body, further increasing the risk of cracking or shattering when heated. Manufacturers of oven-safe ceramics typically ensure that the body and glaze expand at a similar rate and reinforce the structure to withstand the stresses of heating, significantly reducing the risk of thermal shock.
What to Look for When Purchasing Bowls
Material Safety and Compatibility:
Ensure the bowls are made from materials that are safe for food contact and compatible with your intended use, whether for oven baking, microwave heating, or storage. Materials like ceramic, glass, and certain metals should have clear labels regarding their safety and compatibility.
Oven-Safe Designation:
If you plan to use bowls for baking or heating in the oven, check for an oven-safe designation. This indicates the bowl has been tested and can withstand the temperatures of an oven without damage.
Resistant to Thermal Shock:
Look for bowls advertised as resistant to thermal shock, meaning they can handle sudden temperature changes without cracking or breaking. This feature is crucial for kitchenware that will go from one extreme temperature to another.
Even Wall Thickness:
Bowls with even wall thickness are less likely to break due to thermal stress, as they can more evenly distribute heat. Assess the bowl for any thin spots or irregularities in shape that might make it more susceptible to breaking.
Non-Toxic Glazes:
For ceramic bowls, ensure the glazes used are non-toxic and lead-free, especially if the bowls will be used for serving food. This reduces health risks and ensures the safety of your meals.
Warranty or Guarantee:
Manufacturers confident in the durability and quality of their products often offer warranties or guarantees. Look for this when purchasing, as it provides an added layer of protection against defects or unexpected damage.
User Reviews and Recommendations:
Before making a purchase, consider reading user reviews and seeking recommendations. These can provide insights into the durability, performance, and any potential issues with the bowls not apparent at first glance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the suitability of ceramic bowls for oven use is essential for safe and effective cooking experiences. While many ceramic bowls are designed to withstand oven temperatures, it’s crucial to consider factors such as glaze composition and temperature limitations to prevent damage or potential hazards like thermal shock. Utilizing oven-safe ceramic bowls offers numerous benefits, including even heat distribution and the retention of flavors and moisture during cooking. Hopefully, this article gave you some helpful tips about can ceramic bowls go in the oven, so now that you have the proper knowledge on how to get the job done, why not give it a try today?





